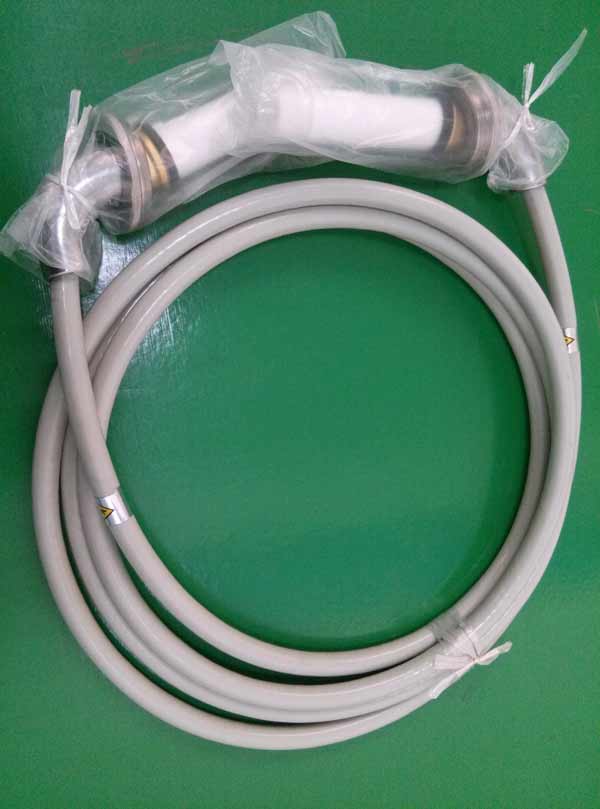
The structure composition and classification of X-ray high voltage cable
Posted by Lillian on
Newheek’s X-ray high voltage cables are available in 75KV and 90KV. 75KV high voltage cable can withstand high voltage at both ends up to 125KV, and 90KV high voltage cable can withstand high voltage at both ends up to 175K.
The structure of the X-ray high-voltage cable: There are two types of separation methods according to the core line: coaxial (concentric circle) and non-coaxial (non-concentric circle).
(1)X-ray high voltage cable Conductive core wire
The innermost layer of X-ray high voltage cable. Each core wire is composed of multiple strands of thin copper wires, which are insulated outwards.
- High voltage insulation layer
Outside the core wire is the main insulation layer of the X-ray high-voltage cable, which is made of rubber and chemical materials, and the thickness is between 4.5-13mm.
(3)X-ray high voltage cable Semiconductor layer
Close to the insulating layer, made of semiconductor material and rubber, gray-black, 1-1.5mm thick.
(4) X-ray high voltage cableMetal shielding layer
It is braided with tinned copper wire with a diameter of not more than 0.3, and the braiding density is not less than 50%, or it is wrapped with tinned copper wire mesh tape, which is closely attached to the semiconductor layer, and the cable is separated and welded to the high-voltage plug horn.
(5)X-ray high voltage cable Protective layer
The outermost layer, made of plastic fragments, is woven with useful black veil and vinylon thread.
If you have any needs, remember to contact us!