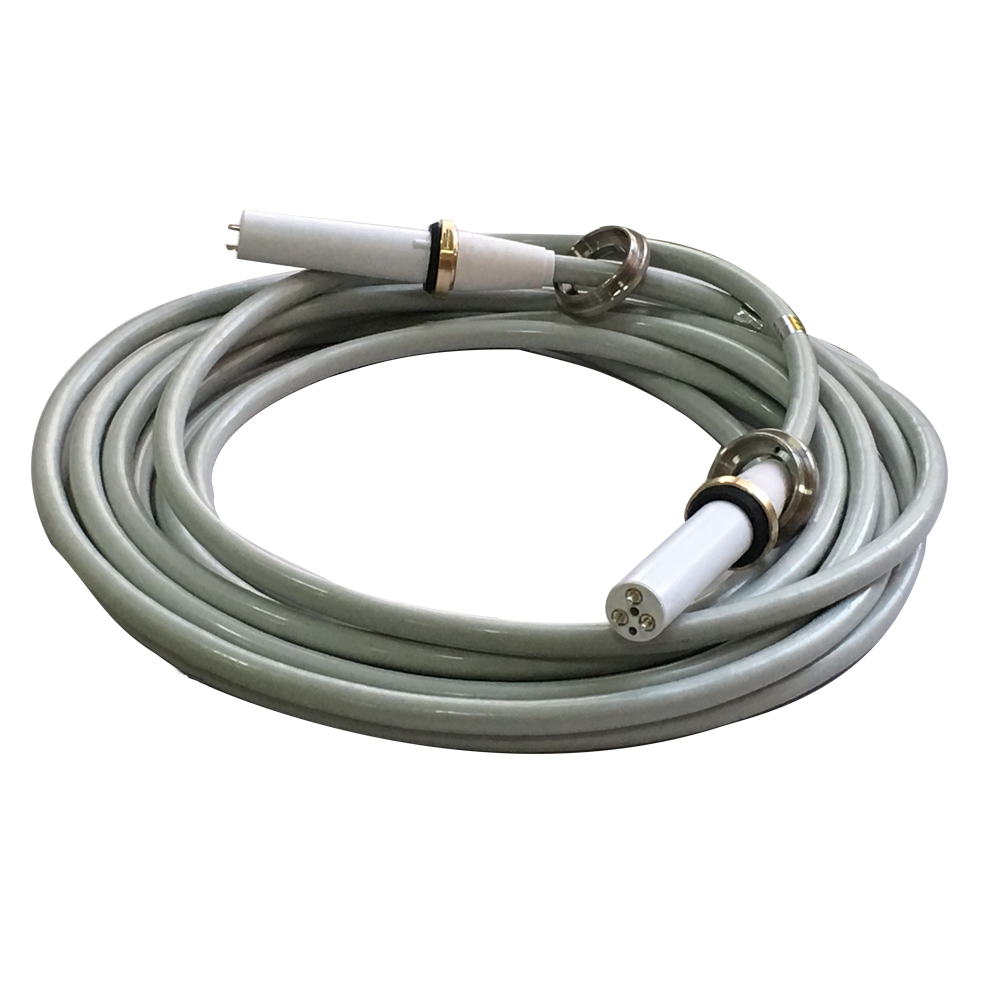
The structure of high-voltage cables for imaging equipment
The high-voltage cable is connected to the high-voltage generator and the X-ray tube head in the large and medium-sized x-ray machine. The function is to send the high voltage output by the high voltage generator to the two poles of the x-ray tube and send the heating voltage of the filament to the filament of the x-ray tube. The structure of high-voltage cables: There are two types of coaxial (concentric circle) and non-coaxial (non-concentric circle) arrangements according to the core line.
(1) Conductive core wire
The innermost layer of high-voltage cables. Each core wire is composed of multiple strands of thin copper wires, and is covered with an insulating skin. Insulation requirements: withstand 50Hz, 1000V alternating current test for 5min without breakdown. Two hearts are designed for single focus X-ray tubes, and three hearts are designed for dual focus X-ray tubes. (There is insulation between each core wire)
(2) High voltage insulation layer
Outside the core wire, is the main insulation layer of the high-voltage cable, which is made of rubber and chemical raw materials, and the thickness is between 4.5-13mm. It has good mechanical strength and toughness, can be bent within a certain range, and the pressure resistance is generally 50-200kV.
(3) Semiconductor layer
Close to the insulating layer, made of semiconductor materials and rubber, gray-black, 1-1.5mm thick. The function is to eliminate the electrostatic field between the outer surface of the insulating layer and the metal shielding layer.
(4) Metal shielding layer
It is braided with tinned copper wire with a diameter of not more than 0.3, and the weaving density is not less than 50%, or it is overlapped with tinned copper wire mesh tape and wrapped tightly on the semiconductor layer. The two ends of the cable are welded to the high-voltage plug horn. Ground through a fixed ring. The role of the metal shielding layer is to prevent electric shock to the operator or patient when the high-voltage cable breaks down to ensure personal safety.
(5) Protective layer
The outermost layer of high-voltage cables is mostly made of plastic, which is thought to be woven with black cotton yarn and vinylon thread. The function is to strengthen the mechanical protection of the cable, reduce external damage, and prevent harmful gas, oil and ultraviolet rays from harming the cable.
If you are interested in our high-voltage cables, welcome to consult.