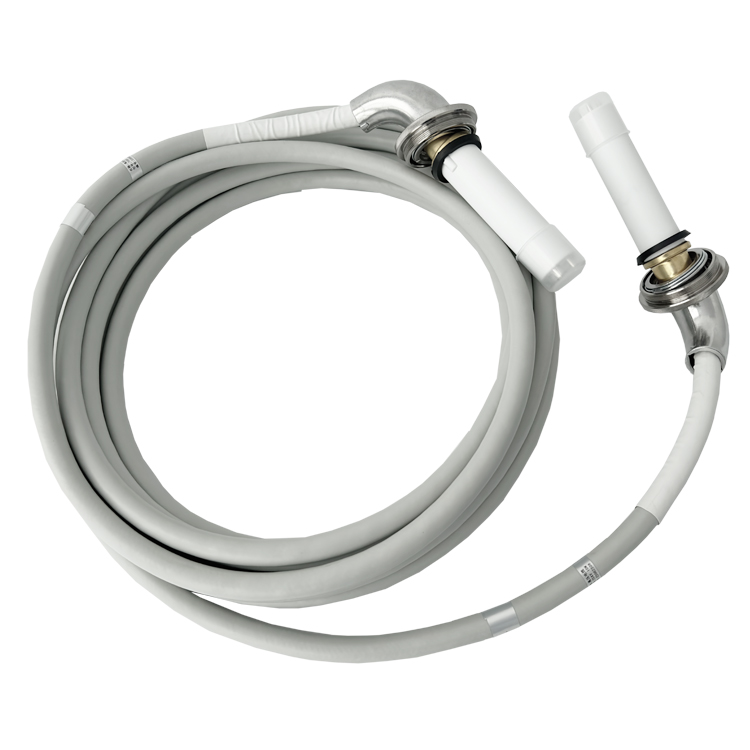
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using solid-core X-ray high-voltage cables compared to stranded-core cables?
Solid-core X-ray high-voltage cables and stranded-core cables are both used in various industries, including medical imaging and industrial testing. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of each:
Advantages of Solid-Core X-ray High-Voltage Cables:
- Higher current carrying capacity: Solid-core cables have a larger cross-sectional area, allowing them to carry higher current loads compared to stranded-core cables.
- Better electrical performance: Solid-core cables generally have lower electrical resistance, resulting in lower voltage drops and better signal transmission.
- Improved stability: Due to their solid construction, these cables can offer better mechanical stability and less susceptibility to vibration compared to stranded-core cables.
- Reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI): Solid-core cables provide better shielding properties, minimizing the risk of EMI and ensuring accurate signal transmission.
Disadvantages of Solid-Core X-ray High-Voltage Cables:
- Limited flexibility: Solid-core cables are less flexible than stranded-core cables, making them more challenging to route in tight spaces or around corners.
- Higher risk of breakage: Solid-core cables are more prone to breakage when subjected to repeated bending or twisting motions.
- Difficult to repair: In the event of damage to the cable, it can be more challenging and time-consuming to repair a solid-core cable compared to a stranded-core cable.
Advantages of Stranded-Core Cables:
- Greater flexibility: Stranded-core cables are more flexible, allowing for easier installation and routing in tight spaces.
- Improved durability: The multiple strands in stranded-core cables can provide added resilience, making them more resistant to breakage and fatigue caused by repeated bending or twisting.
- Ease of repair: When damaged, stranded-core cables are generally easier and quicker to repair compared to solid-core cables.
Disadvantages of Stranded-Core Cables:
- Lower current carrying capacity: Stranded-core cables have a smaller cross-sectional area, limiting their ability to carry higher current loads compared to solid-core cables.
- Higher electrical resistance: Due to the presence of multiple strands, stranded-core cables typically have higher electrical resistance, resulting in higher voltage drops and potentially impacting signal quality.
- Increased susceptibility to EMI: Stranded-core cables may provide less effective EMI shielding compared to solid-core cables, potentially leading to signal degradation in certain applications.
Overall, the choice between solid-core and stranded-core X-ray high-voltage cables depends on specific application requirements, such as the desired current capacity, flexibility needs, and susceptibility to EMI.
If you are interested in our high-voltage cables, Welcome to contact us.
Email :service@newheek.com
Tel:+86 18953679166 ; Whatsapp:+86 18953679166